

When a matrix is transposed, its rows and columns are switched like this:
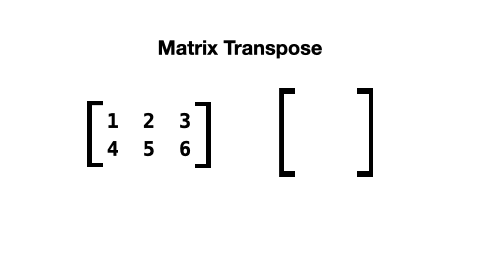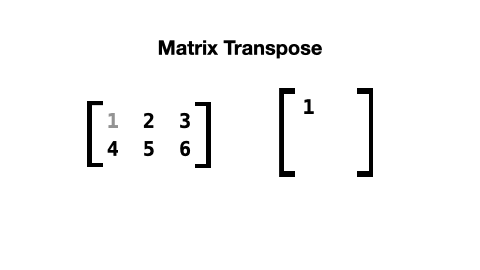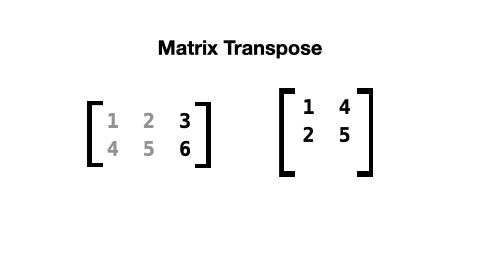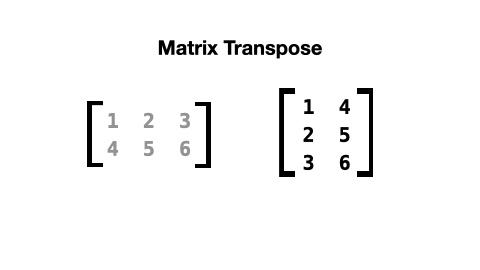
The list comprehension to do this looks like this:
def transpose_matrix(matrix):
return [[row[col] for row in matrix] for col, _ in enumerate(matrix[0])]
The matrix should have a rectangular form. All rows should be of equal size and all columns should be of equal size.
Here is a test program that uses the transpose function:
matrix = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]
]
def print_matrix(matrix):
for row in matrix:
print(" ".join([str(col) for col in row]))
print()
def transpose_matrix(matrix):
return [[row[col] for row in matrix] for col, _ in enumerate(matrix[0])]
print_matrix(matrix)
transposed_matrix = transpose_matrix(matrix)
print_matrix(transposed_matrix)
transposed_again_matrix = transpose_matrix(transposed_matrix)
print_matrix(transposed_again_matrix)
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 1 4 2 5 3 6 1 2 3 4 5 6